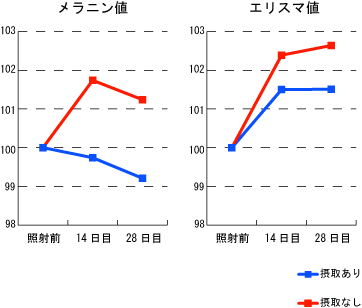
A clinical observation was conducted to assess the impact of NKG Kefir consumption on skin pigmentation caused by ultraviolet (UV) irradiation.
Study Design
-Prior to starting NKG Kefir intake, UV irradiation was applied to the inner side of one upper arm of participants, producing minimal erythema (mild skin redness).
-Pigmentation levels on this arm were measured at 2 weeks and 4 weeks post-irradiation using a Mezzameter (a device that quantifies melanin and erythema).
-At the start of NKG Kefir intake, UV irradiation was similarly performed on the inner side of the opposite upper arm. Pigmentation was measured again at 2 weeks and 4 weeks after irradiation while participants were regularly consuming NKG Kefir.
Key Findings
-Compared to the arm exposed before kefir intake, the arm exposed during kefir consumption showed a significant decrease in melanin levels (pigmentation) and erythrema levels (redness).
-This suggests that regular intake of NKG Kefir reduces UV-induced pigmentation and skin redness over time.
Implications
-NKG Kefir may contribute to skin protection and recovery following UV exposure.
-It holds potential as a functional food supporting skin health, especially for individuals concerned with sun damage and pigmentation issues.
(Blue = Kefir, Red = Control)